A Complete Guide To Falls
Falls and a fear of falling can diminish your ability to lead a full and independent life. A fall can result in unwanted outcomes, including injury, loss of independence, and decreased ability to do the things that are most important to you. You can prevent falling by doing physical activities you enjoy and working with a physical therapist to improve your balance, muscle strength, and endurance.
Although 1 in every 4 older adults falls each year, falling is not a part of normal aging. A physical therapist can help you assess your risk factors and develop a plan to address them and remain independent by:
- Designing an individualized plan for your fall-prevention needs.
- Helping you make your home as safe as possible.
- Educating you about the medical risk factors associated with falls.
- Providing you with appropriate exercises and balance training.
- Working with other health care professionals to address any underlying medical conditions that could increase your fall risk.
- Providing you with recommendations on appropriate community programs.
Physical therapists are movement experts who improve quality of life through hands-on care, patient education, and prescribed movement.
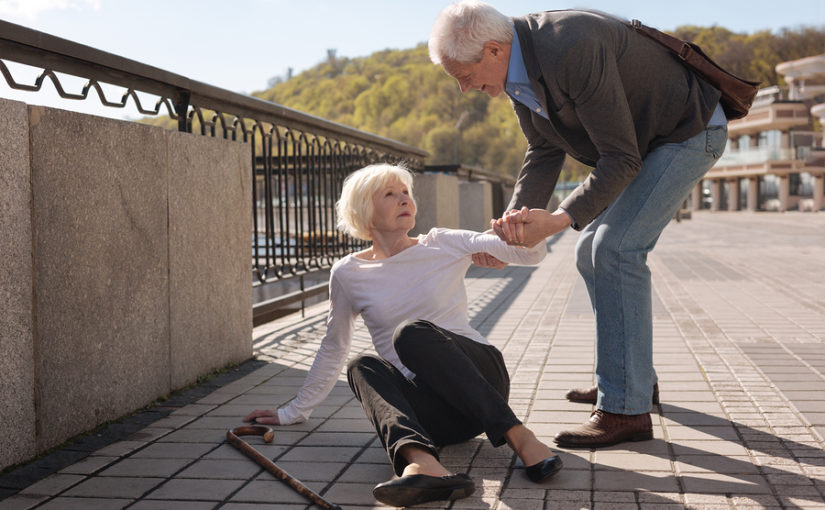

What Are Falls?
A fall is defined as any event that leads to an unplanned, unexpected contact with a supporting surface, such as the floor or a piece of furniture, that is not the result of a push or shove or the result of a medical event, such as a heart attack or fainting.
A near-fall is a stumble or loss of balance that would result in a fall if you were unable to catch yourself.
There are lots of factors that can increase your risk for falls, including:
How Is It Diagnosed?
Unlike with other medical conditions, there is no single test that can predict a fall. Adults aged 65 years and older should be screened by their primary care provider on a yearly basis to help determine their risk for falling. Additionally, if you are worried about falling, have had a loss of balance, or have had a fall, you should see a physical therapist.
How Can a Physical Therapist Help?
A physical therapist can conduct a brief check (“screening”) of your fall risk. If the screening shows that you are at risk, the therapist will perform a thorough evaluation, including:
Based on the evaluation results, your physical therapist will design a plan that is tailored to your needs. Your treatment plan may include:
Balance training. Balance training has been shown to be an important and effective part of falls prevention. Your physical therapist will design exercises that challenge your ability to keep your balance as well as recover from a loss of balance, including exercises such as single-leg standing, or holding your balance while performing an action like reciting the alphabet.
Walking and moving. A prescribed exercise program should include a walking program. However, starting a walking program with poor balance can actually increase your risk for falling. Talk to your doctor or a physical therapist before you initiate a walking program to make sure that it is the right choice for you.
While working with a physical therapist, you may be asked to perform activities, such as:
Doing more than one thing at the same time—safely. Older adults who have difficulty walking and talking at the same time are at a higher risk of falling. To help increase your safety during daily activities, your physical therapist can design a “dual-task” training program. This kind of training will challenge you to maintain walking speed, while you perform another task, such as counting backward, engaging in a conversation, or carrying a bag of groceries.
Strength training. Strengthening is a key element of fall prevention and is very effective in preventing falls, especially when combined with balance exercises. Your physical therapist will design an individualized strengthening program that focuses on specific muscle groups to help improve your standing balance, your balance while walking, and your ability to recover from a loss of balance.
Endurance training. Aerobic exercise is physical exercise of relatively low intensity and long duration; it can help improve almost every aspect of your health, especially your endurance. Your physical therapist can work with you to plan a safe aerobic program, such as a walking or an aquatic program, to address your specific needs. The program may start with as little as 10-minute sessions and progress to 30-minute sessions, as your endurance improves.
Pain management. Pain management plays a crucial role in older adults’ risk for falling and quality of life. Certain exercises, such as strengthening and aerobic exercises, are appropriate interventions to relieve pain in addition to decreasing fall risk. Treatments need to be modified appropriately, depending on each individual’s source of pain. Physical therapy has been shown to help individuals reduce or eliminate their need for pain medication, including opioids.
Education. Your physical therapist will take the time to explain how you can best manage your own risks for falling. Your therapist also may talk to you about the best activities to help maintain your quality of life, and offer educational resources, such as:
Fear management. It is important for you to talk with your physical therapist about the fear you have of falling. The therapist will work with you to build your confidence and help you get back to the activities that you may be avoiding because you are afraid of falling. Your individual assessment can also identify the activities that you actually should avoid to stay safe.
Community programs. Several community-based fall-prevention programs are promoted by the Injury Prevention and Control Center of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in collaboration with the Administration on Aging. These programs help people:
These programs often are led by volunteer coaches. Your physical therapist may be involved in setting up one of these programs or can help you find programs in your area that are best for you.
Personal recommendations. Your physical therapist can provide personal recommendations based on your condition and goals to help you: